| [1] Pezet D, Michel P, Rebischung C, et al. Cancer of the stomach. Gastroenterol Clin Biol. 2006;30(2):16-23.
[2] Brenner H, Rothenbacher D, Arndt V. Epidemiology of stomach cancer. Methods Mol Biol. 2009;472: 467-477.
[3] Crookes P, Leichman CG, Leichman L, et al. Systemic chemotherapy for gastric carcinoma followed by postoperative intraperitoneal therapy: a final report. Cancer. 1997;79(9):1767-1775.
[4] Bozzetti F, Yu W, Baratti D, et al. Locoregional treatment of peritoneal carcinomatosis from gastric cancer. J Surg Oncol. 2008;98(4):273-276.
[5] Newman E, Potmesil M, Ryan T, et al. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy, surgery, and adjuvant intraperitoneal chemotherapy in patients with locally advanced gastric or gastroesophageal junction carcinoma: a phase II study. Semin Oncol. 2005;32(6 Suppl 9):S97-100.
[6] Xu DZ, Zhan YQ, Sun XW, et al. Meta-analysis of intraperitoneal chemotherapy for gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 2004;10(18):2727-2730.
[7] 孔勇.腹腔内化疗对结直肠癌术后肝转移的疗效观察[J].右江医学,2005,33(3):237-239.
[8] 罗景慧,杨迎暴,李经才,等.顺铂在家兔体内的时间药动学[J].中国药理学通报,1999,15(4):363-365.
[9] 刘华顶,王世亮,俞敏,等.氟尿嘧啶植入剂胃癌术后腹腔缓释化疗的药动学研究[J].癌症进展,2012,10(1):73-79.
[10] 中国知网.中国学术期刊总库[DB/OL].2013-08-10.https://www.cnki.net
[11] 仇爱峰,施育华.进展期胃癌术中区域性植入氟尿嘧啶缓释剂预防术后复发和转移的临床研究[J].吉林医学,2012,33(31):6778-6779.
[12] 吴江,陈海军.术中动脉灌注化疗联合术野5-氟尿嘧啶缓释剂植入预防进展期胃癌术后肝脏转移及局部复发的疗效研究[J].中国医药科学,2012,2(20):19-20.
[13] 魏海云,周玮,黄凯.术中区域性植入缓释氟尿嘧啶预防进展期胃癌术后复发和转移[J].中国老年学杂志,2012,32(12):2478-2480.
[14] 余雄,万焱华.术中植入缓释氟尿嘧啶预防胃癌术后复发[J].实用临床医学,2010,11(10):51-53.
[15] 张为民,徐光辉,巨爱平,等.含奥沙利铂方案治疗晚期胃癌的临床观察[J].癌症,2003,22(12):1346-1348.
[16] 刘福坤,李国立,陈忠豪,等.胃癌术前介入治疗的临床和病理观察(附250例报告)[J].南京大学学报(自然科学版),1998,34(2):167-171.
[17] 沈惠琳,叶泉忠.选择性动脉插管化疗+碘油栓塞治疗30例中晚期胃癌的临床疗效对比观察[J].杭州师范学院学报(医学版),2008,28(4):238-240.
[18] 潘彦康.胃癌介入化疗与全身化疗的疗效比较[J].吉林医学,2009,30(15):1561-1562.
[19] 武振明,齐秀恒,刘琪.联合草酸铂经动脉介入治疗晚期胃癌疗效观察[J].中国肿瘤临床与康复,2007,14(4):337-339.
[20] 赵予军,简国庆,吕素兰.奥沙利铂联合亚叶酸钙、5-氟尿嘧啶治疗晚期胃癌的临床研究[J].中国医药导报,2007,4(10):22-23.
[21] Siddik ZH. Cisplatin: mode of cytotoxic action and molecular basis of resistance. Oncogene. 2003;22(47):7265-7279.
[22] 孙勇,叶蕾,张理星,等.药物控制释放体系的应用进展[J].山东医药工业,2002,21(6):19-22.
[23] 曾敬,赵桂贞,段纪东.药物控制释放的研究进展[J].化学通报(网络版),2006,69(1):w032.
[24] 邬思辉,苏政权.壳聚糖及其衍生物作为药物载体研究进展[J].现代生物医学进展,2008,8(8):1588-1591.
[25] 冯慧,严晓燕.用于缓释、控释、靶向制剂的新型材料[J].中国药物应用与监测,2007,4(3):53-56.
[26] 任建东,刘松青,王章阳.胶原蛋白作为蛋白类药物载体系统的应用[J].中国药业,2005,14(5):16-17.
[27] 丁清.两种药物控释载体的体外释药性能[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(32):6351-6354.
[28] 王标兵.药物缓释载体用温敏性水凝胶[J].高分子通报,2006,(11):85-91.
[29] 盛卫忠,张延伟,张轶斌,等.血清CA72-4、CA19-9及CEA免疫放射量度分析在胃癌诊治中的意义[J].上海医科大学学报,2000,27(2):94-97.
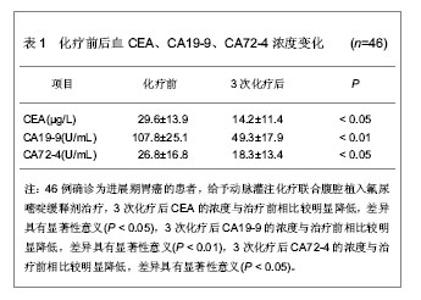
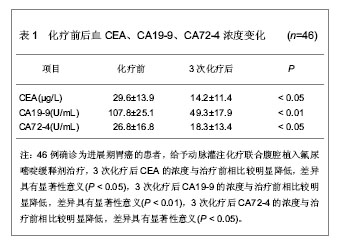
[30] 张成武,邹寿椿,裘华森,等.胃癌预后指标的多因素回归分析[J].中华胃肠外科杂志,2002,5(2):113-116.
[31] 刘福坤,李国立,黎介寿,等.Ⅲ、Ⅳ期胃癌新辅助化疗后再手术疗效的临床研究[J].外科理论与实践,2003,8(1):25-27.
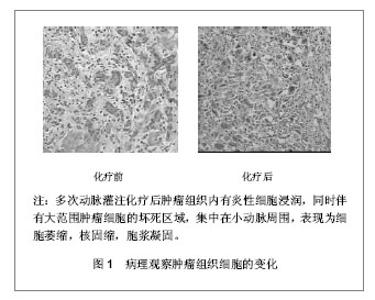
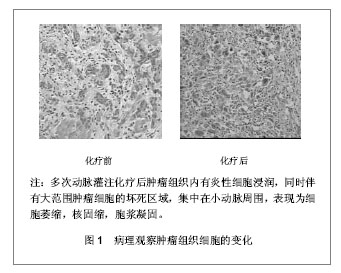
[32] Satomi D, Takiguchi N, Koda K, et al. Apoptosis and apoptosis-associated gene products related to the response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy for gastric cancer. Int J Oncol. 2002;20(6):1167-1171.
[33] Eriguchi M, Nonaka Y, Yanagie H, et al. A molecular biological study of anti-tumor mechanisms of an anti-cancer agent Oxaliplatin against established human gastric cancer cell lines. Biomed Pharmacother. 2003;57(9):412-415. |